Mode 1
Household socket and Extension Cord
The Electric vehicle is connected to the power grid through standard 230 Volt- 15 Ampere household pin socket. Charging operation at maximum power over several hours will increase wear on the socket and increase the likelihood of fire. Electrical injury or risk of fire are much higher if the fuse board is not protected by an RCD. Heating of the socket and cables following intensive use for several hours at or near maximum power (which varies from 8 to 16 Amp depending on the country.)


Mode 2
Non-deficated socket with Cable-incorporated Protection Device
The Electric Vehicle is connected to the main power grid Via household Socket-outlets. Charging is done via a single- phase or three-phase network and installation of an earthing cable. A IC-CPD (In cord control & protection device) is built into the cable. This Solution is more expensive than Mode 1 due to added circuitry in the circle.
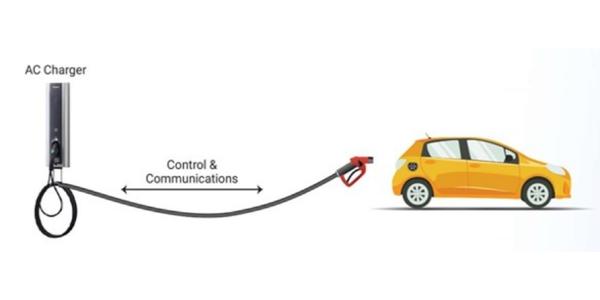
Mode 3
Fixed, Dedicated Circuit-Socket
The Electric Vehicle is connected directly to the electrical network via Specific Socket and plug and a dedicated circuit. A Control and protection function is inbuilt in the equipment. Typically, Mode 3 type of charging is done by AC chargers. This is Slow/moderate mode of charging.
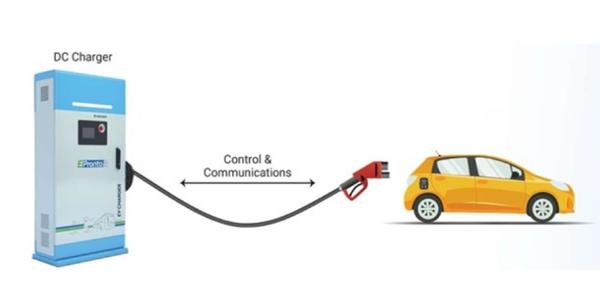
Mode 4
DC Connection
The Electric vehicle is connected to the main power gird through an external charger. Control and protection functions are inbuilt in the charger. Typically, Mode 4 type of charging is done by High rating DC chargers. This is FAST mode of charging. In mode 4 different type of sockets are used depending upon the standard adopted by vehicle manufacture for example. CHAdemo, GB/T or CCS.
